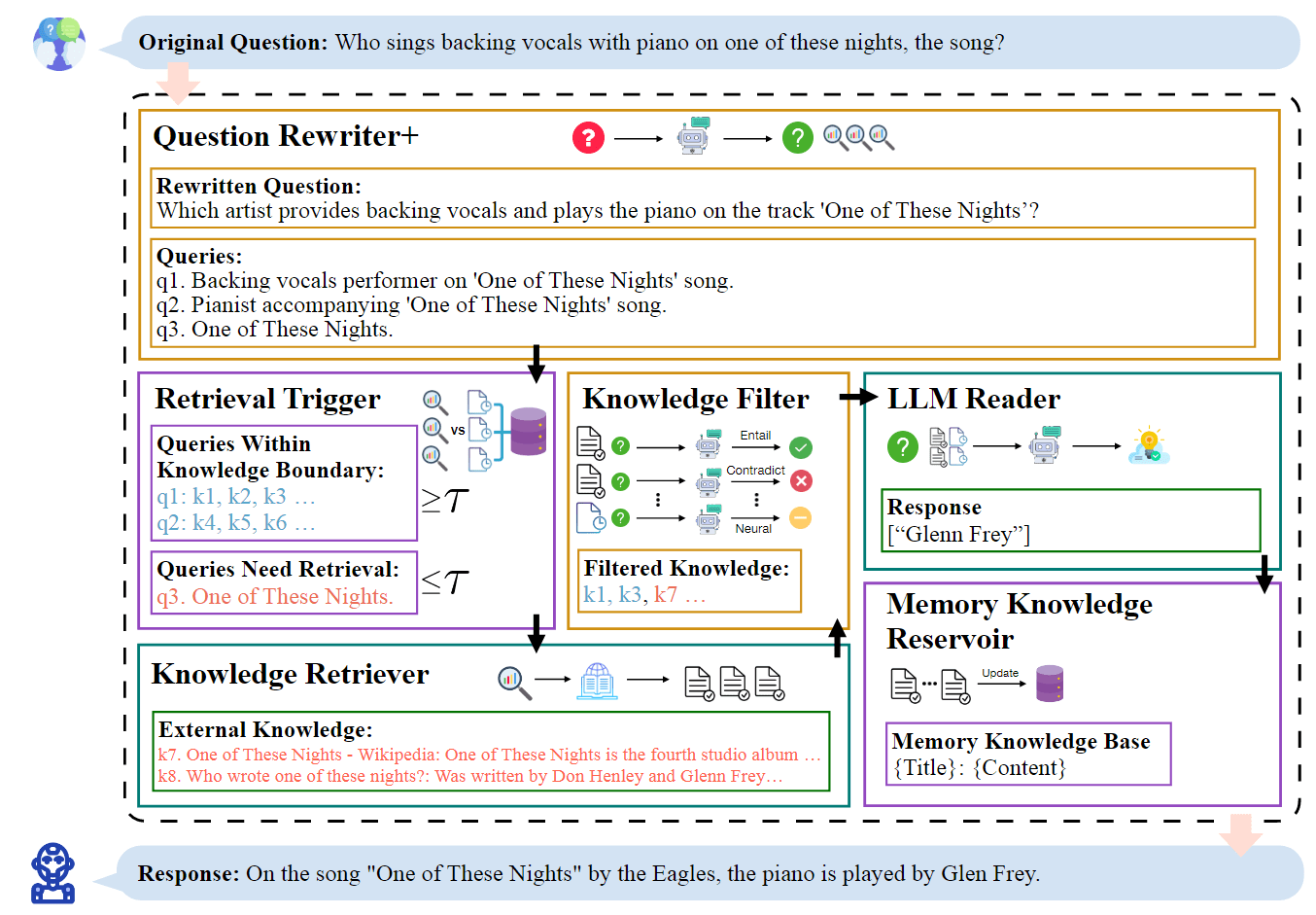
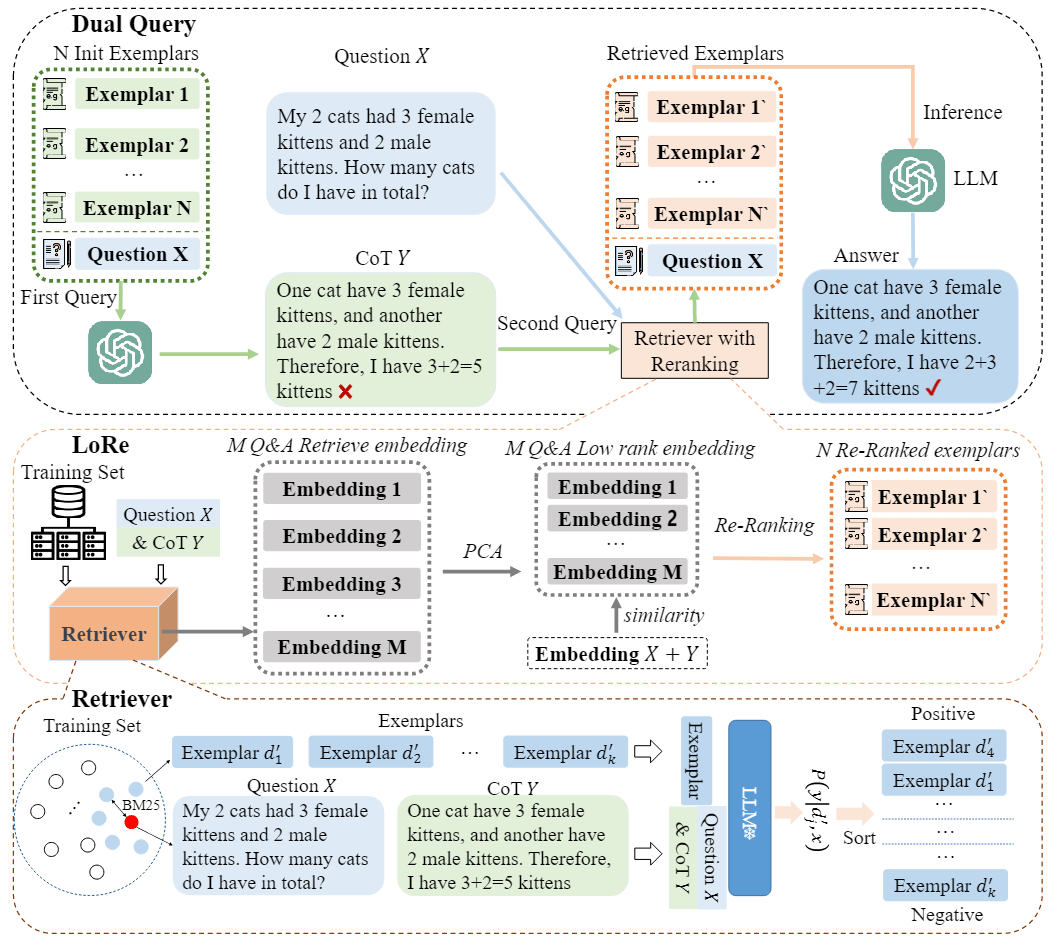
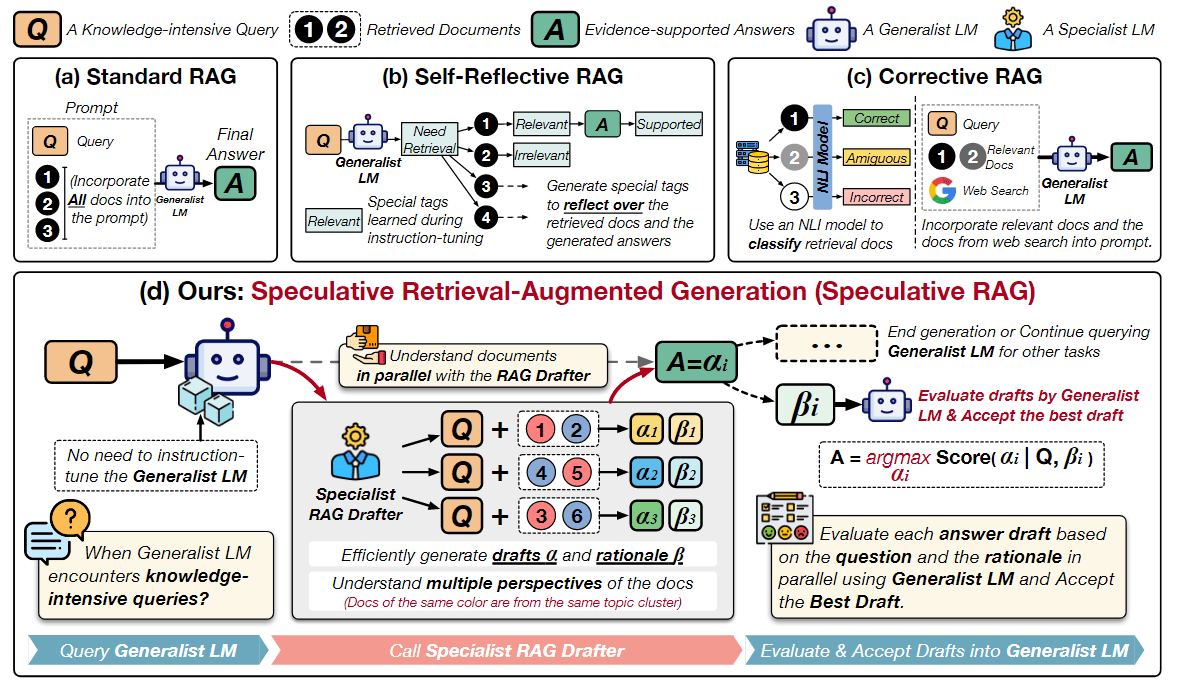
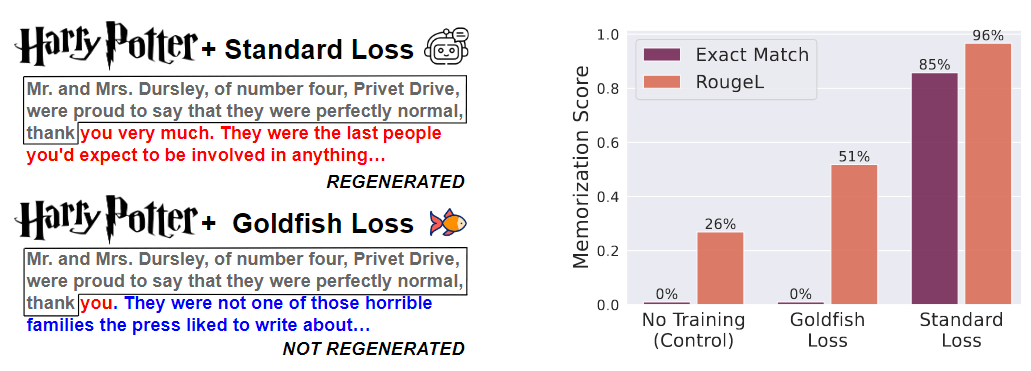
谐音字典构建方案 计算词语与词语之间的音距,将音距相近的词语聚到一块,从而构造出一个谐音字典。通过该谐音字典,我们可以快速获取指定词语 top k 个谐音词语。
要达成这个目标,我们首先要有一个词典。通过整合目前已有的全部数据集,并对数据集进行清洗,包括去除重复的数据,滤除特殊符号、表情等。然后再对清洗后的数据进行分词、词频过滤,最终得到一个尽可能完备的词典。
全部数据集:/nfs/users/chenxu/project/OpenNMT-tf/asr_correct/data/food_redbook_wiki_dataset.txt
分词后结果:/nfs/users/chenxu/project/OpenNMT-tf/asr_correct/data/data_word_list.json
词频过滤后结果:/nfs/users/chenxu/project/OpenNMT-tf/asr_correct/data/word_count_filtered_dict.json
接下来,就是最麻烦的谐音字典构建环节。
前置知识 本节介绍构建谐音字典所需的第三方包以及构建过程中涉及的一些基础内容。
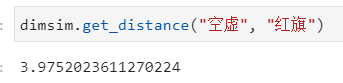
音距计算 借助 dimsim 包,我们可以获取任意两个词语之间的音距,例如“空虚”与“红旗”之间的音距。
拥有计算音距的方式后,即可设定阈值,将指定阈值范围内的词语对设置为谐音字,我们可以将其组织为字典的形式,其格式如下所示:
Ray Ray 是一个高性能的分布式执行引擎,开源的人工智能框架,目标之一在于:让开发者可以用一个运行在笔记本电脑上的原型算法,仅需添加数行代码就能轻松转为适合于计算机集群运行的(或单个多核心计算机的)高性能分布式应用。
借助 Ray 可以快速编写多进程程序,这对于大数据的处理非常有用,因为当词典越大,我们构建的谐音字典内容越丰富,所需的时间也越久。
构建方案 通过前面的步骤,我们已经得到一个包含词频的词典,接下来要做的就是计算两两词语之间的音距,从而构建谐音字典。
原始方案 最容易想到的方法是双循环,让每一个词语与另一个词语依次计算音距。该方法在词典规模较小时是切实可行的。
【实现代码】:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 import dimsimfrom collections import defaultdictword_sim_dict = defaultdict(list ) dis_threshold = 5 for word in word_list: for _word in word_list: if word == _word: continue sim_dis = dimsim.get_distance(word, _word) if sim_dis < dis_threshold: word_sim_dict[word].append((_word, sim_dis))
但是当词典规模较大,例如达到 15w 时,所需的构建时间达到了惊人的 480 小时!因此,我们需要想办法降低时间复杂度!
首先,考虑是否可以消除一些重复计算。显然,上述代码中存在大量的重复计算,例如“红旗”与“空虚”计算了一遍音距之后,不需要再计算“空虚”与“红旗”之间的音距。因此,此时就有两种改进方案。
方案一:将已经计算过音距的词语对进行记录,当再次遇到时直接读取结果。
方案二:将 word_sim_dict 修改为 Orderedict(有序字典),在双循环过程中只计算一遍“红旗”与“空虚”的音距。当完成循环后,再遍历有序字典,将缺失的数据(“空虚”与“红旗”的音距)补齐。
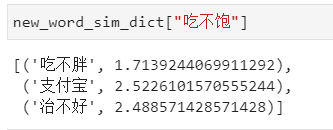
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 new_word_sim_dict = defaultdict(list ) for item in list (word_sim_dict.items()): word, sim_list = item if len (sim_list) == 0 : continue for sim_item in sim_list: word_sim, sim = sim_item new_word_sim_dict[word_sim].append((word, sim)) new_word_sim_dict[word].append((word_sim, sim))
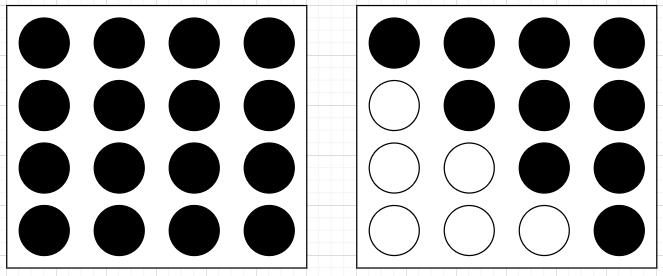
该方案相当于从图左的全部计算转变为图右的计算对角线及以上,计算量近乎减少了一半。但这样仍然远远不够,我们还需要有更好的方案。
改进方案 在双循环的大框架改动不了(似乎没有能够将时间复杂度降低到 O(n log n)的方式)的前提下,可行的方案唯有1. 继续减少计算量;2. 添加多进程或多线程。
【问】:那么如何继续减少计算量呢?
【答】:首先让我们思考一下为什么要使用双循环?因为我们无法得到当前词语(“红旗”)与哪些词语是谐音字,因此只能让它与非自身的所有词语都计算一遍音距。如果我们能够知道词语的一些信息,例如拼音等等,从而缩小范围来达到减少计算量的目的(例如“红旗”和“你好”这对词语肯定不算是谐音字典)。
【问】:这样的话,是不是可以对词语的拼音做一次聚类?
【答】:我之前尝试过,这非常的麻烦,首先要知道 dimsim.get_distance 函数是如何计算音距,然后再利用 pypinyin 去获取词语的 pinyin,这对于字数较短的词语是可行的,但对于长度 4 以上的词语就非常麻烦了。因此,我采用的是区域划分的方案,下面就听我细细道来。
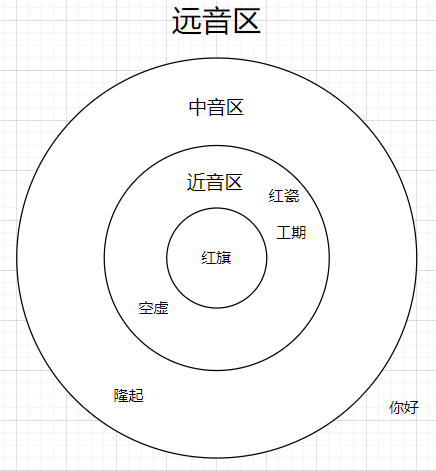
区域划分方案 首先,从词典中按顺序挑选一个词语,计算该词语与其他所有词语的音距,然后根据音距划分区域,将其分为近音区、中音区和远音区。
对于当前词语来说,近音区内的所有词语与当前词语可以构造为谐音词对,例如“空虚”和“红瓷”都是“红旗”的谐音词对。
对于近音区内的所有词语,中音区内的词语和近音区内的其他词语都可能是该词语的谐音词,例如“红瓷”与“工期”可以构成谐音词对。但需要注意的是,近音区内的词语不一定都是谐音词对,例如“空虚”与“红瓷”位于“红旗”的两端,虽然它们与“红旗”的音距小于设定的谐音词对阈值,但它们之间的音距却会大于设定的谐音词对阈值。
通过区域划分的方式,我们有效地减少了近音区内词语的计算量,因为它们只需要遍历“红旗”近音区和中音区内的词语,而无需计算与远音区各词语之间的音距。
添加多进程 近音区内词语的音距遍历是相互独立的,因此我们可以在其中加入多进程,分别计算“空虚”、“红瓷”和“工期”与其他词语的音距。在这里我们借助 Ray 来实现多进程。
完整代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 import osimport jsonimport dimsimimport jsonlinesimport pickleimport tqdmimport rayimport timefrom collections import defaultdict@ray.remote def execute_batch (word: str , word_sim_list: list , area_word_list: list , threshold: int = 5 ): word_synonym_dict = {} word_set = set () for word_sim in word_sim_list: sim_word_list = get_sim_word_list(word_sim, area_word_list, threshold=threshold) sim_word_list.append(word) word_synonym_dict[word_sim] = sim_word_list word_set.add(word_sim) return word_synonym_dict, word_set def get_sim_word_list (word: str , word_list: list , threshold: int ) -> list : sim_word_list = [] for _word in word_list: if word == _word: continue sim = dimsim.get_distance(word, _word) if sim <= threshold: sim_word_list.append((_word, sim)) return sim_word_list class SynonymBuilder : def __init__ (self, area_dis_threshold: int = [5 , 15 ], thread_nums: int = 4 ): self.word_set = set () self.word_synonym_dict = {} self.area_dis_threshold = area_dis_threshold self.thread_nums = thread_nums ray.init(num_cpus=thread_nums, ignore_reinit_error=True ) def _split_word_sim_area (self, word: str , word_list: list ) -> dict : area_dict = { "c" : [], "m" : [], "f" : [] } for _word in word_list: if word == _word: continue sim = dimsim.get_distance(word, _word) if sim <= self.area_dis_threshold[0 ]: area_dict["c" ].append((_word, sim)) elif sim <= self.area_dis_threshold[1 ]: area_dict["m" ].append(_word) else : area_dict["f" ].append(_word) return area_dict def _get_sim_word_list (self, word: str , word_list: list ) -> list : sim_word_list = [] for _word in word_list: if word == _word: continue sim = dimsim.get_distance(word, _word) if sim <= self.area_dis_threshold[0 ]: sim_word_list.append((_word, sim)) return sim_word_list def run_one (self, word: str , word_list: list ) -> None : word_area_dict = self._split_word_sim_area(word, word_list) word_sim_list = [item[0 ] for item in word_area_dict["c" ]] self.word_synonym_dict[word] = word_area_dict["c" ] self.word_set.add(word) batch_size = (len (word_sim_list) + self.thread_nums - 1 ) // self.thread_nums ray_executor_list = [] for batch_index in range (self.thread_nums): start, end = batch_index * batch_size, (batch_index + 1 ) * batch_size ray_executor_list.append(execute_batch.remote( word, word_sim_list[start: end], word_sim_list + word_area_dict["m" ])) for executor_item in ray_executor_list: batch_word_synonym_dict, batch_word_set = ray.get(executor_item) self.word_set = self.word_set | batch_word_set for batch_word, batch_word_sim_list in batch_word_synonym_dict.items(): self.word_synonym_dict[batch_word] = batch_word_sim_list def run (self, word_list: list ) -> None : word_length = len (word_list) time_start = time.time() for word in word_list: time_end = time.time() print ("=" * 80 ) print ("目前已完成的词语数:{},总数:{},当前进度:{:.2f}%,花费时间" .format (len (self.word_set), word_length, len (self.word_set) / word_length), time_end - time_start) if word in self.word_set: continue self.run_one(word, word_list) if __name__ == '__main__' : project_dir = "/nfs/users/chenxu/project/OpenNMT-tf/asr_correct" print ("加载数据..." ) with open (os.path.join(project_dir, "data/word_count_filtered_dict.json" ), "r" , encoding="utf-8" ) as file: word_count_dict = json.load(file) print ("开始获取长度 2 的词语..." ) word_list = [] for word, count in tqdm.tqdm(word_count_dict.items()): word_len = len (word) if word_len == 2 : word_list.append(word) print ("构建长度 3 的谐音字典..." ) synonym_builder = SynonymBuilder() synonym_builder.run(word_list) with open (os.path.join(project_dir, "data/word_sim_dict_test_2.pkl" ), "wb" ) as file: pickle.dump(synonym_builder.word_synonym_dict, file)