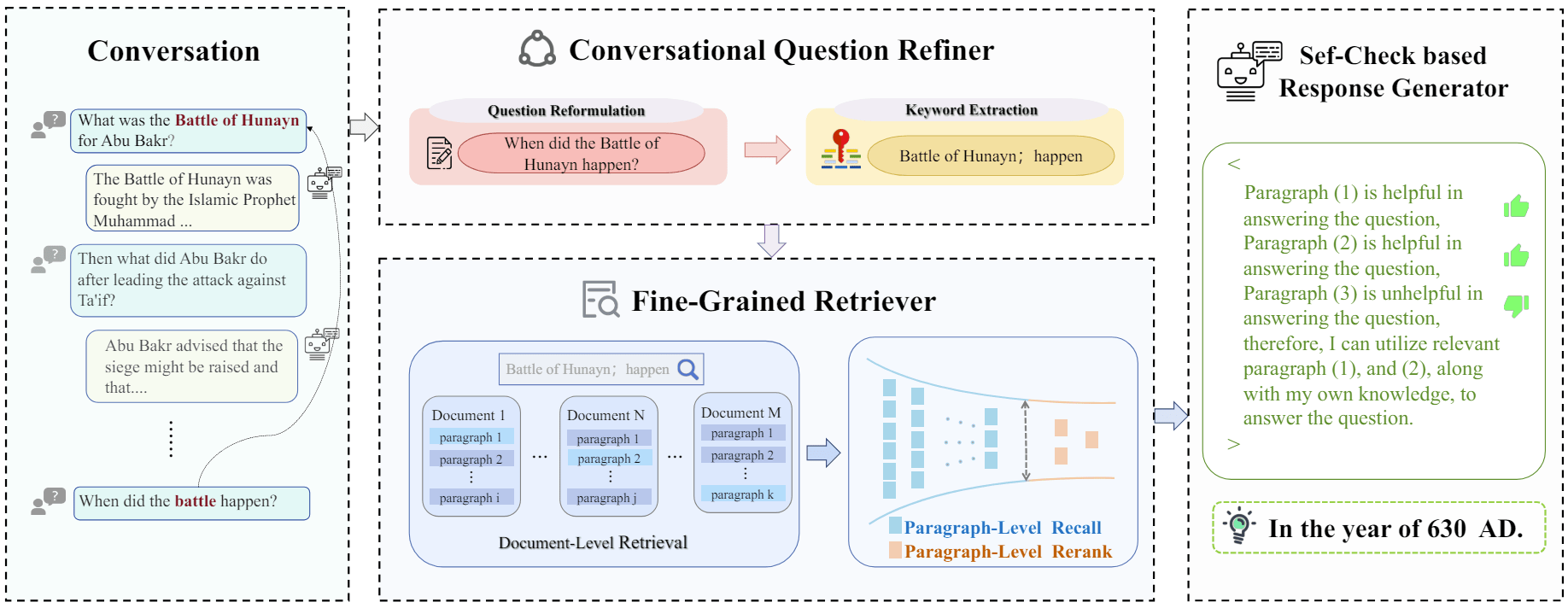
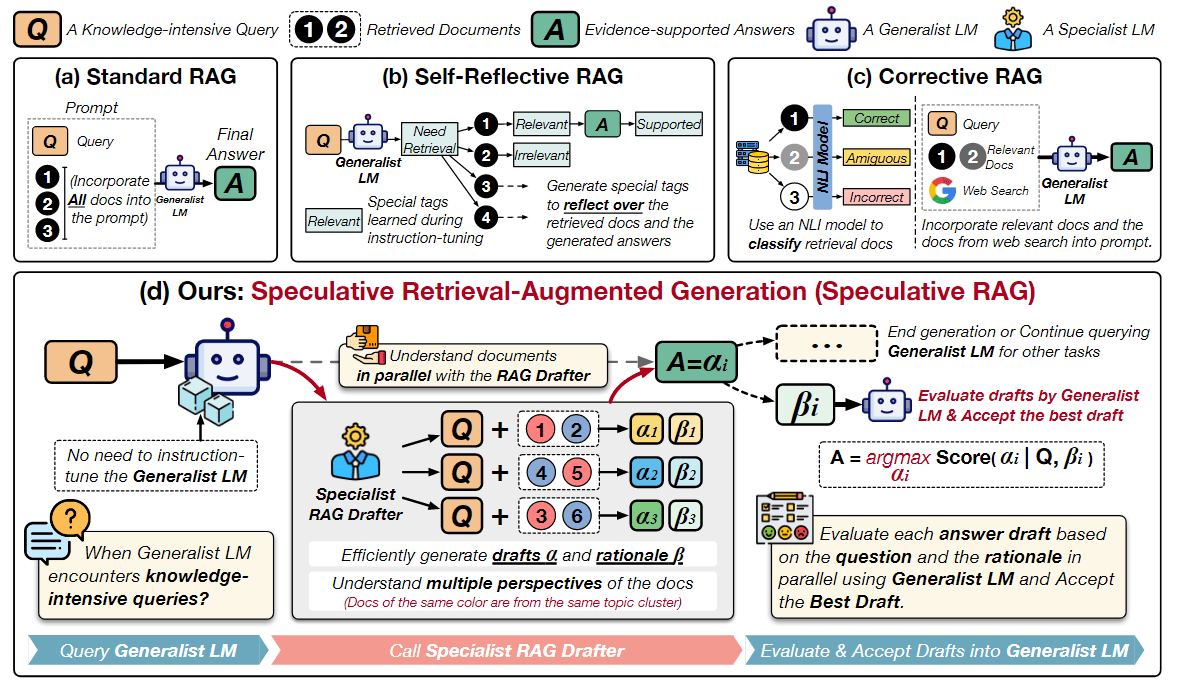
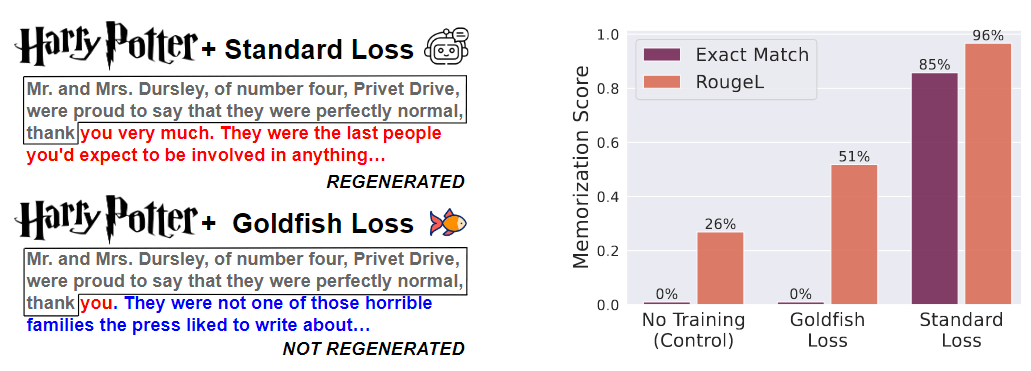
RAG 查询检索模块 - 检索 - 混合检索
虽然向量检索有助于检索给定查询的语义相关块,但它有时在匹配特定关键字词方面缺乏准确性。
为了解决这个问题,混合检索是一种解决方案。该策略充分利用了矢量搜索和关键字搜索等不同检索技术的优势,并将它们智能地组合在一起。使用这种混合方法,您仍然可以匹配相关的关键字,同时保持对查询意图的控制。 **混合搜索的案例,可以参考Pinecone的入门指南[3]**。
Pinecone 混合检索方案
该博客讨论了混合搜索的概念和实现,混合搜索结合了矢量搜索(密集检索)和传统搜索方法的优势,以提高信息检索性能,尤其是在缺乏用于微调模型的特定领域数据的情况下。
- 矢量搜索与传统搜索: 当使用特定领域的数据集对模型进行微调时,矢量搜索在检索相关信息方面表现出色。然而,由于缺乏经过微调的模型,矢量搜索在处理“域外”任务时显得力不从心。传统的搜索方法,如 BM25,可以处理新的领域,但在提供类似人类的智能检索方面能力有限。
混合搜索解决方案: 该博客介绍了一种将密集(向量)和稀疏(传统)搜索方法结合为混合搜索方法的解决方案。这种方法旨在利用矢量搜索的性能潜力,同时保持传统搜索对新领域的适应性。
实现过程
使用支持单一稀疏密集索引的 Pinecone 演示了混合搜索的实施。这种方法简化了结合密集和稀疏搜索引擎所需的工程设计工作,并允许通过 alpha 参数轻松调整密集和稀疏结果之间的权重。

步骤 1:数据集准备
本博客将介绍如何为混合搜索准备一个数据集(使用 Hugging Face Datasets 的 pubmed_qa 数据集),包括创建数据的密集和稀疏向量表示。
1 | from datasets import load_dataset # !pip install datasets |
数据格式如下所示:
1 | Dataset({ features: ['pubid', 'question', 'context', 'long_answer', 'final_decision'], num_rows: 1000 }) |
步骤 2:稀疏向量
稀疏向量嵌入是通过标记化逻辑创建的,博客选择了一种使用 Hugging Face Transformers 的 BERT 标记化器的直接方法。
1 | from transformers import BertTokenizerFast # !pip install transformers |
由于我们只进行 tokenize,因此需要 input_ids,并将输入 ID 表示转换为整数 ID 值的唯一单词或子词 token。Pinecone 期望接收字典格式的稀疏向量。例如,向量:
1 | [0, 2, 9, 2, 5, 5] |
每个 token 由字典中的单个 key 表示,并且其频率由相应的 value 来计数。作者对 input_ids 应用相同的转换,如下所示:
1 | from collections import Counter |
1 | {101: 1, 16984: 1, 3526: 2, 2331: 2, 1006: 10, ... } |
可以将所有这些逻辑重新格式化为两个函数:
build_dict:将输入 ID 转换为字典;generate_sparse_vectors:处理标记化和字典创建。
1 | def build_dict(input_batch): |
在 generate_sparse_vectors 函数中指定 special_tokens=False 来删除特殊 token 101、102、103和0。这些都是 BERT Transformer 模型明确要求的 token,但在构建稀疏向量时没有任何意义。
步骤 3:密集向量
密集向量嵌入使用 sentence transformer 模型(”multi-qa-MiniLM-L6-cos-v1”)生成,可为每个上下文生成 384 维密集向量。
1 | # !pip install sentence-transformers |
步骤 4:创建稀疏密集索引
该博客详细介绍了如何在 Pinecone 中创建和使用稀疏密集索引,包括使用稀疏向量和密集向量倒插数据。
1 | import pinecone # !pip install pinecone-client |
要使用启用稀疏-密集的索引,必须将 pod_type 设置为 s1 或 p1,并将 metric 设置为使用点积。
步骤 5:进行查询
混合搜索中的查询包括查询的密集向量和稀疏向量表示。该博客演示了如何执行查询和调整 alpha 参数,以平衡密集和稀疏搜索结果的影响。

1 | def hybrid_scale(dense, sparse, alpha: float): |
文章结论
混合搜索通过与传统搜索方法相结合,为克服矢量搜索在域外场景中的局限性提供了一种很有前途的方法。这篇博客为实现混合搜索提供了全面的指导,通过智能地结合矢量和传统搜索方法,强调了混合搜索在改进各领域信息检索方面的潜力。